soil moisture sensors for agriculture
Soil moisture sensors for agriculture estimate the volume of water content based on the dielectric constant of the soil. The dielectric constant indicates the soil’s capability to transmit electricity. As the water content of the soil increases, the dielectric constant of the soil increases, because the dielectric constant of water is much larger than the other soil components, including air. Therefore, the measurement of the dielectric constant gives a predictable assessment of water content.

Any farmer will tell you that the conditions of the soil change constantly throughout the growing season. The soil conditions are influenced by the weather, row density, crop patterns. During this period, the plants are continuously changing and adapting to the environment. The plant’s roots and shoots grow in soil most advantageous to growth.
Soil Moisture Sensors Instruction Manual
Farmers are now using soil moisture sensors for agriculture to monitor particular sectors of the field, enabling them to react quickly to changes in the land and crops. The use of smaller and less-complex sensors is making quick response possible. This allows farmers to turn soil sensor readings, weather, and historical crop data into actionable perception by seeing the bigger picture.

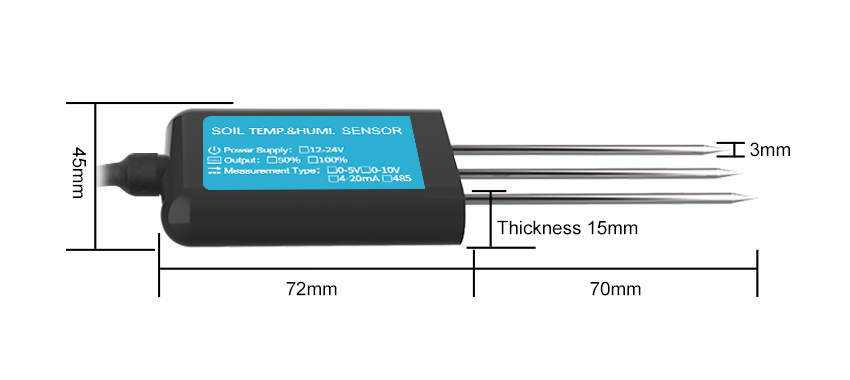
Most soil sensors are single-point sensors. They take a measurement at a single location. A single point sensor can measure soil moisture and temperature, or soil moisture, temperature and salinity. The sensor can be completely buried in the soil. Some sensors measure volumetric water content for the length of the sensor.
It’s important to measure soil moisture at multiple depths in order to optimize irrigation, as it indicates the penetration of water all through the root zone. The main benefit of using a soil profiling probe is the reduction of costs of installing multiple single-point sensors, and the requirement to dig a large hole to bury them at the proper depths.
Sensors that measure volumetric water content are often referred to as soil moisture sensors. Soil volumetric water content sensors measure the water content of soil. Farmers use soil moisture sensors to monitor how much irrigation is needed to reach the desired amount of water in the soil. Soil sensors can be quickly acquired or installed for long-term measurements.
The amount of moisture or soil water is important to know because soil water performs as a carrier of food nutrients needed for plant growth. Soil water is a nutrient by itself. The yield of a crop is most often influenced by the amount of water available rather than the deficit of other food nutrients. Water regulates soil temperatures. Microorganisms require water for their metabolic activities, while helping in the chemical and biological activities of the soil. Finally, water is essential for photosynthesis. Therefore, soil moisture sensors are critical for Agriculture.