Understand Smart Irrigation
Smart irrigation have emerged as a solution, revolutionizing the way we water our landscapes. This article explores the concept of smart irrigation, delving into its features, benefits, working principles, and applications. By harnessing the power of technology, smart irrigation systems ensure optimal water usage, resulting in healthier plants, lower water consumption, and greener landscapes.

Features of smart irrigation:
Smart irrigation systems incorporate several key features that set them apart from traditional methods:
1.1. Weather-based adjustments: These systems can access real-time weather data, including temperature, humidity, and precipitation forecasts. By using this information, they can adjust watering schedules accordingly, ensuring that plants receive just the right amount of water.
1.2. Soil moisture sensors: Smart irrigation systems employ sensors to measure the moisture content in the soil. By continuously monitoring soil conditions, the systems can provide precise and targeted irrigation, avoiding both overwatering and underwatering.
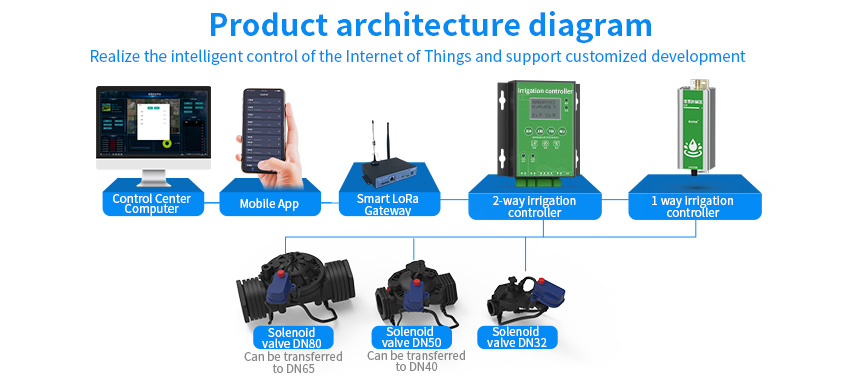
1.3. Automated scheduling: Unlike manual irrigation methods, smart irrigation systems automatically manage watering schedules based on plant requirements, weather conditions, and user-defined settings. This eliminates the need for constant monitoring and manual adjustment.
1.4. Remote control and monitoring: Many smart irrigation systems can be accessed and controlled remotely through mobile apps or web-based interfaces. This provides users with the flexibility to manage their irrigation systems from anywhere at any time.
Working principles of smart irrigation system:
Smart irrigation systems rely on a combination of sensors, data analysis, and automation to optimize water usage. Here is an overview of the working principles:
2.1. Weather data analysis: The system collects weather data from reliable sources or weather stations. By analyzing this data, the system can determine how much water the landscape requires and adjust the watering schedule accordingly.
2.2. Soil moisture sensing: Soil moisture sensors are strategically placed in the landscape to measure the moisture content at different depths. These sensors provide real-time feedback to the system, allowing it to determine the exact watering needs of the plants.
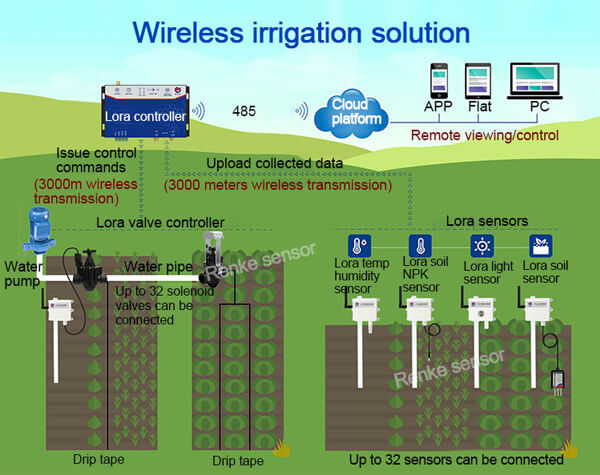
2.3. Evapotranspiration calculation: Evapotranspiration is the combined loss of water through evaporation from the soil and transpiration from plants. Smart irrigation systems use algorithms to calculate evapotranspiration rates based on weather and plant-specific data. This calculation guides the system in determining the optimal watering duration and frequency.
2.4. Drip irrigation and zone control: Smart irrigation systems often utilize drip irrigation techniques, which deliver water directly to the root zone of plants. Additionally, the system can divide the landscape into different irrigation zones, each with its own watering requirements. This zone control ensures that water is distributed precisely where and when it is needed.
Applications and benefits of smart irrigation system:
3.1. Residential landscaping: Smart irrigation systems are widely used in residential settings, ensuring efficient watering of lawns, gardens, and flower beds. Homeowners can achieve beautiful landscapes without wasting water or excessive manual effort.
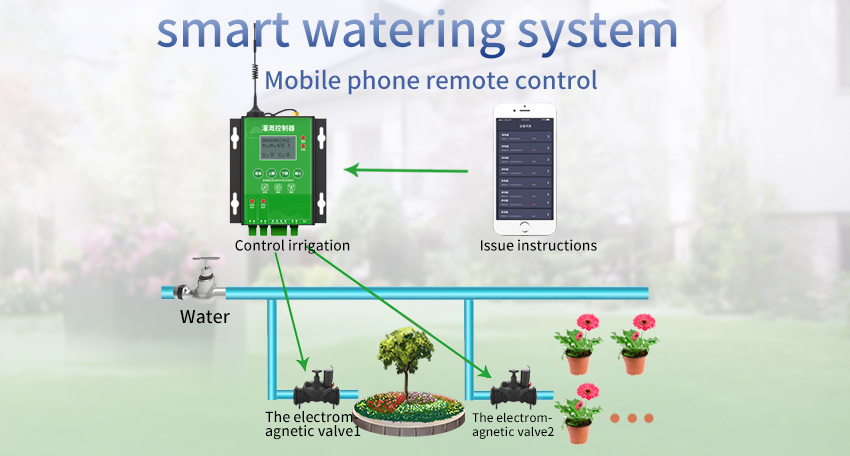
3.2. Commercial landscaping: Landscapes in commercial areas, such as parks, golf courses, and corporate campuses, benefit greatly from smart irrigation systems. The systems help maintain visually appealing landscapes while minimizing water consumption and irrigation costs.
3.3. Agricultural irrigation: Smart irrigation techniques are increasingly adopted in agricultural practices. Farmers can optimize water usage, improve crop yield, and reduce water expenses by employing these systems in large-scale farming operations.
3.4. Public parks and green spaces: Smart irrigation systems are instrumental in maintaining public parks and green spaces. By conserving water and ensuring the health of plant life, these systems contribute to the sustainability and beauty of urban environments.
Environmental and economic benefits:
4.1. Water conservation: By precisely delivering the right amount of water to plants, smart irrigation systems help conserve water resources. This reduces strain on local water supplies and promotes sustainable water management practices.
4.2. Reduced water expenses: Efficient water usage leads to reduced water bills, making smart irrigation systems cost-effective in the long run. Users can save significant amounts of money by avoiding overwatering and reducing water waste.
4.3. Improved plant health: Smart irrigation systems promote healthier plant growth by providing appropriate levels of hydration. By avoiding overwatering, plants are less susceptible to diseases, root rot, and other water-related issues.