In recent years, the agriculture industry has been facing increasing pressure to adopt more sustainable and environmentally friendly farming practices. With the growing global population and the need to produce more food with limited resources, farmers are turning to technology to help them improve their productivity while minimizing their impact on the environment. One such technology that has been gaining traction in the agriculture industry is soil sensors. These devices are revolutionizing the way farmers monitor and manage their soil, allowing them to make more informed decisions and ultimately improve their farming practices.
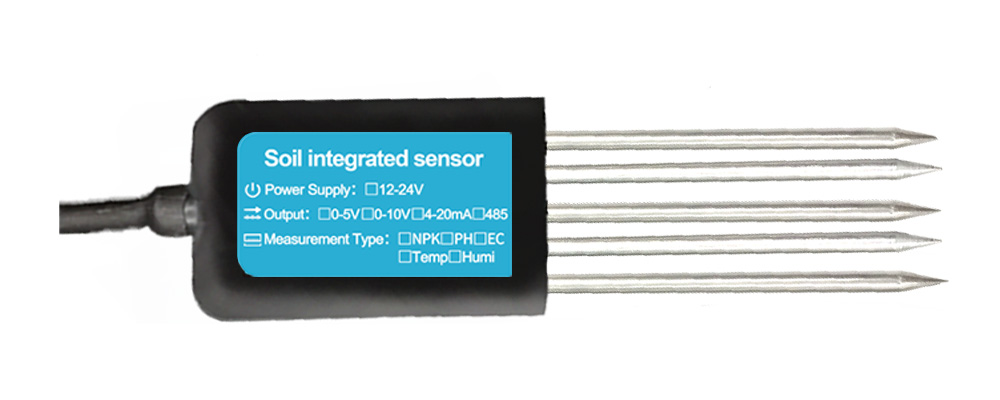
What are Soil Sensors?
Soil sensors are devices that are used to measure various parameters of the soil, such as moisture levels, temperature, pH, and nutrient content. These sensors can be placed directly in the soil, either at the surface or at various depths, and are capable of providing real-time data on the condition of the soil. This information is then transmitted to a central system, where it can be analyzed and used to make decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and other farming practices.
The Role of Soil Sensors in Sustainable Farming Practices
Soil sensors play a crucial role in sustainable farming practices by allowing farmers to optimize their use of resources and minimize their impact on the environment. By providing real-time data on soil moisture levels, for example, soil sensors enable farmers to precisely manage their irrigation systems, ensuring that they only use as much water as necessary and avoid overwatering. This not only helps to conserve water, but also reduces the risk of soil erosion and nutrient leaching, which can have harmful effects on the environment.
Similarly, soil sensors can help farmers to optimize their use of fertilizers and other inputs by providing accurate information on the nutrient content of the soil. By knowing exactly what the soil needs, farmers can avoid over-fertilization, which can lead to nutrient runoff and water pollution, and ensure that their crops receive the right nutrients at the right time. This not only helps to protect the environment, but also saves farmers money by reducing their input costs.
In addition to optimizing resource use, soil sensors can also help farmers to improve their crop yields and quality. By providing real-time data on soil conditions, these devices enable farmers to make more informed decisions about planting, harvesting, and other farming practices, ultimately leading to better outcomes. This can have a significant impact on the sustainability of farming operations, as it allows farmers to produce more food with fewer resources, reducing their environmental footprint and contributing to global food security.
Challenges and Opportunities
While soil sensors have the potential to revolutionize the agriculture industry, there are still some challenges that need to be addressed in order to fully realize their benefits. One of the main challenges is the cost of these devices, which can be prohibitive for many small-scale farmers. However, as the technology continues to advance and become more widely adopted, the cost of soil sensors is expected to decrease, making them more accessible to a wider range of farmers.
Another challenge is the complexity of the data that soil sensors produce. While these devices can provide a wealth of information about the soil, farmers may struggle to interpret and use this data effectively. To address this challenge, there is a growing need for user-friendly software and tools that can help farmers to make sense of the data and use it to inform their decision-making.

Despite these challenges, soil sensors also present numerous opportunities for the agriculture industry. For example, the data collected by these devices can be used to inform the development of new farming practices and technologies, such as precision agriculture and smart irrigation systems. This has the potential to revolutionize the way that food is produced, making farming more efficient, sustainable, and environmentally friendly.
Conclusion
Soil sensors are playing an increasingly important role in sustainable farming practices, helping farmers to optimize their use of resources, improve their crop yields, and minimize their impact on the environment. While there are still some challenges to be addressed, the potential benefits of this technology are significant, and it is expected to continue to gain traction in the agriculture industry in the coming years. As farmers continue to adopt soil sensors and use the data they provide to inform their decision-making, the agriculture industry is likely to become more sustainable and environmentally friendly, ultimately contributing to global food security and the well-being of the planet.
